
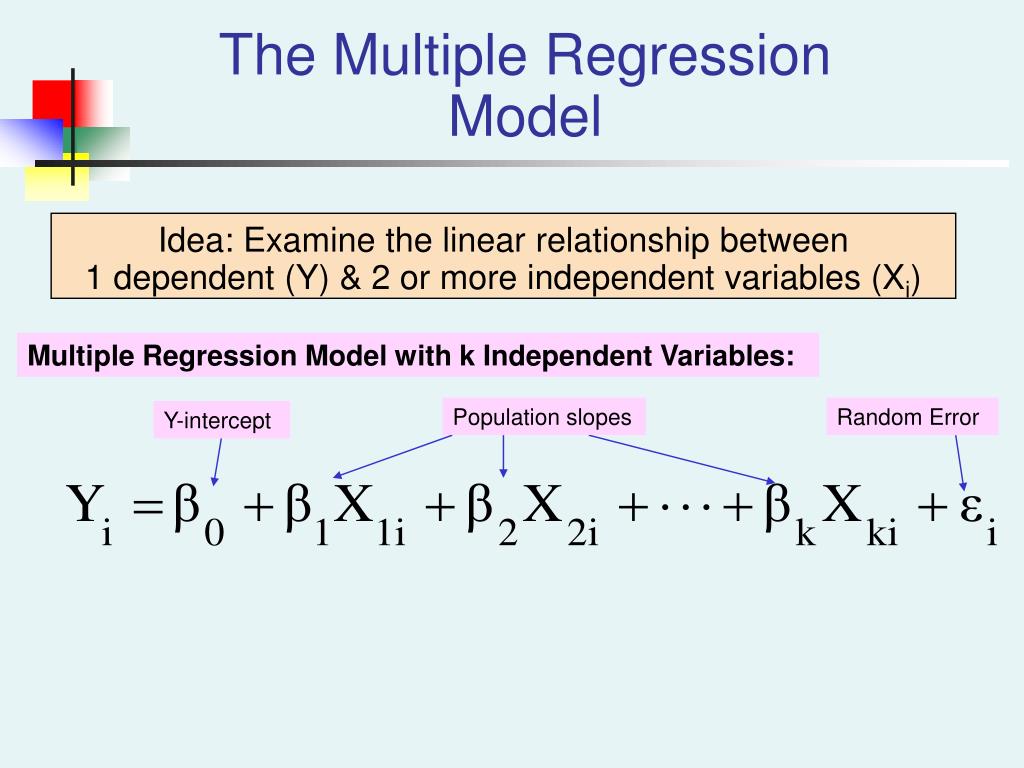
Question 6 1 pts Taking the natural logs of the left and right-hand variables in a regression equation: turns a multiplicative relationship into an additive one tums an additive relationship into a multiplicative one makes the relationship nonlinear so you cannot estimate it using OLS increases the R-squared MacBook Air R. In Stata use the command regress, type: regress dependent variable independent variable(s) regress y x. 215: YB0 + B1ln(X) + u A 1 change in X is associated with a change in Y of 0. Technically, linear regression estimates how much. Taken from Introduction to Econometrics from Stock and Watson, 2003, p.

If you do not see the menu on the left please click here. If the data have a curvy (nonlinear) relationship, but we fit a straight line (linear regression), then o assumption CR3 fails assumption CR2 fails we get a poor predictor of the outcome variable we get a low R-squared any of these might be correct MacBook Air E E R D F G H B N Interpretation of logarithms in a regression. The t-statistic in the Stata output is based on what null hypothesis? O Nobody knows what Stata is talking about It depends on what null hypothesis of the researcher is positing O Bk 70 O Bk = 0 OBk = 1 Question 2 1 pts MacBook Air & 5 R. This gives you a recipe for finding unknown Y when you know X. Transcribed image text: Suppose that you regress y on Xin Stata. It typically means finding a surface parametrised by known X such that Y typically lies close to that surface.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
